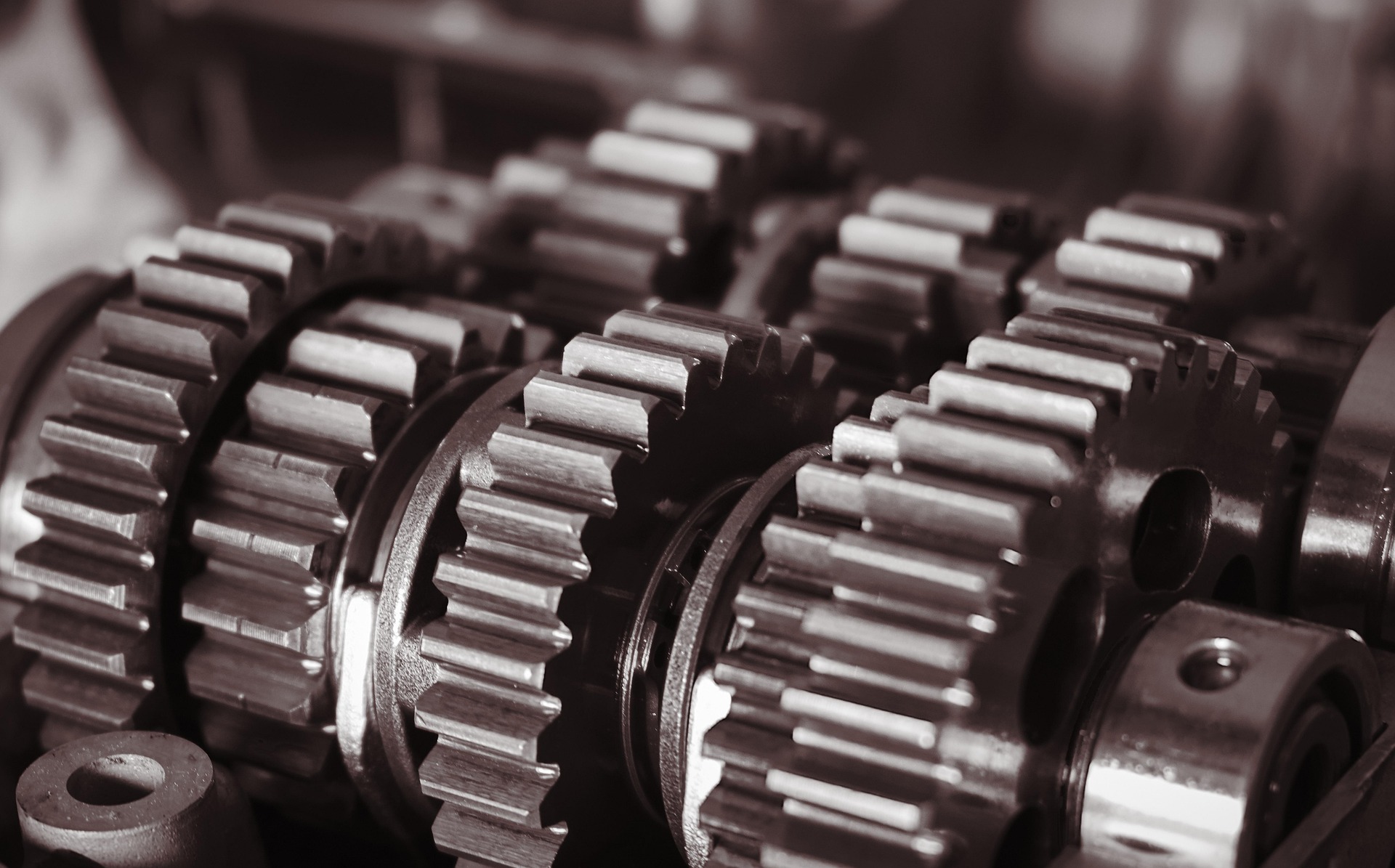
Gear oil is a specialized lubricant formulated to protect gears under high-pressure and high-friction conditions typically found in gearboxes, differentials, and transmissions. Its primary role is to reduce wear between gear teeth, minimize friction, and prevent metal-to-metal contact that can lead to damage or failure. Gear oils are usually thicker than engine oils, offering high film strength to handle heavy loads and shock conditions. They also help dissipate heat and prevent the formation of deposits that could impair gear function. Key features of gear oil include high viscosity, excellent thermal stability, strong load-carrying capacity, and resistance to oxidation and foaming.
Additives for gear oil
Additives play a critical role in enhancing gear oil performance. Extreme Pressure (EP) additives, such as sulfur-phosphorus compounds, protect gears under heavy loads by forming a protective film. Anti-wear additives reduce metal surface wear, while oxidation inhibitors extend oil life. Rust and corrosion inhibitors safeguard metal parts from moisture, and anti-foam agents prevent lubricant breakdown due to aeration.